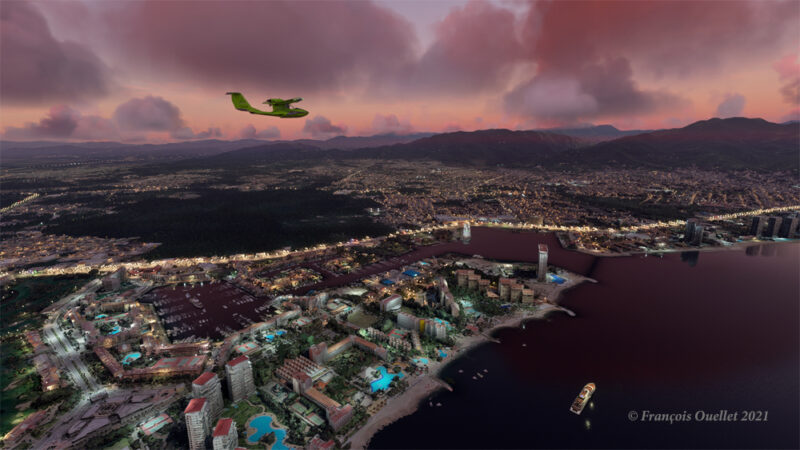
The flight simulation with Microsoft Flight Simulator lets you fly over the planet like never before from the comfort of your own home. As airports around the world transmit weather observations at all times, it’s possible to import this data into the flight simulator and fly virtually in the real weather conditions reported around the globe.
This data enhances the feeling of reality for the virtual pilot, but at the same time complicates his task, as he has to take into account the presence of thunderstorms and icing, surface and upper-level winds, changes in cloud cover, visibility, pressure, and so on.
Today’s virtual pilot must also anticipate that failures of all kinds may affect the flight, especially if he or she owns a high-quality virtual aircraft. The engine(s) may fail, a structural problem may affect the aircraft’s controls and navigation equipment may cease to function. Good planning is essential, just as in real life. And since the brain doesn’t differentiate too much between the real and the virtual, there’s plenty of fun to be had.
So, I’ve decided to fly around the world as a millionaire, at my own pace, i.e., using the types of aircraft that tempt me, and flying the routes that are of particular interest. All of this will be done in real weather, with all its joys and obstacles. I’ll be publishing one of these routes on my blog from time to time.
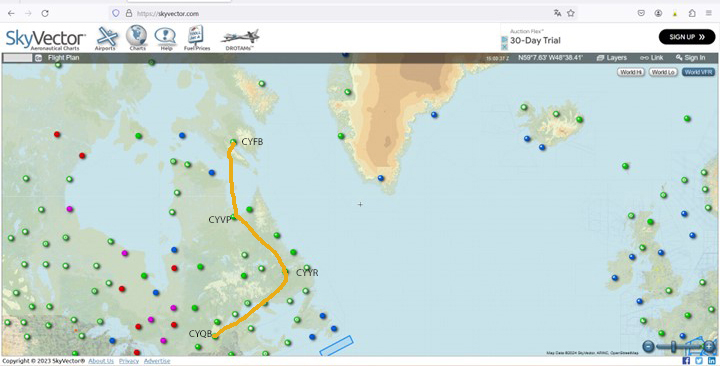
The initial route departs from Quebec’s Jean-Lesage airport (CYQB), passes through Goose Bay (CYYR), in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador, heads north to Kuujjuaq and ends in Iqaluit (CYFB).
Virtual Flight 2 will present a few photos of the Atlantic crossing from Iqaluit to Kangerlussuaq (BGSF) in Greenland, to Isafjordur (BIIS) in Iceland .
Isafjordur airport has a challenging approach. I don’t know if the Cessna Citation Longitude will be able to land there in one piece, but I intend to give it a try.
Virtual flight 1.
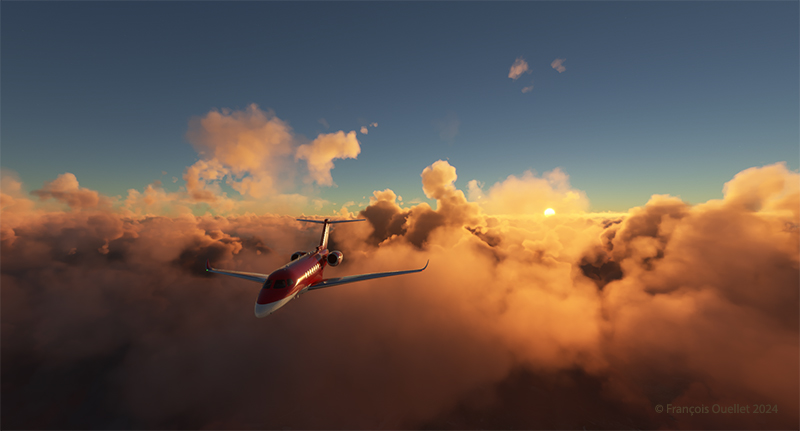

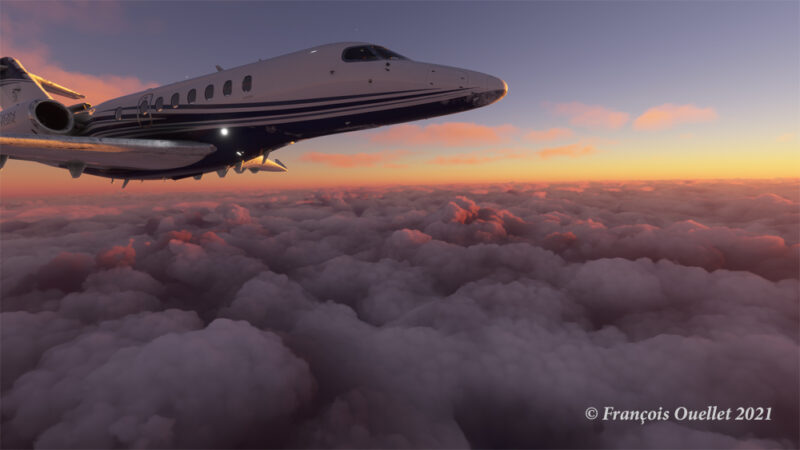
Above, the setting sun illuminates the clouds and the Cessna Citation Longitude en route from Quebec City to Goose Bay. At high altitude, the pilot sets the altimeter to the standard atmospheric pressure of 29.92 inches of mercury. Since all the other pilots are doing the same, a safe separation between the aircraft is ensured.
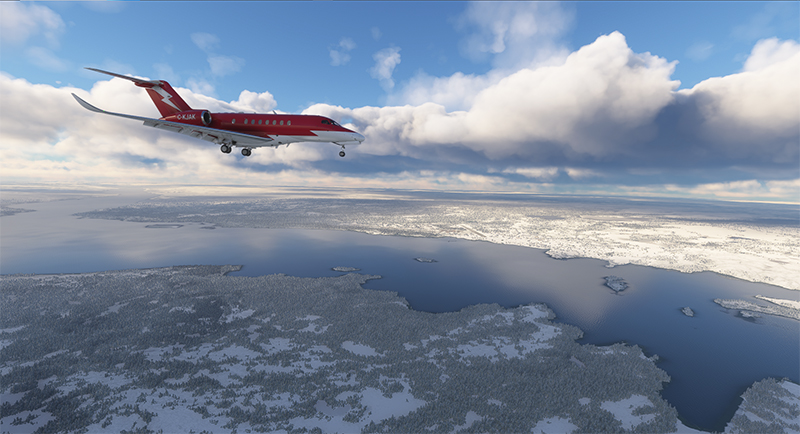

The next day, the aircraft is seen approaching Kuujjuaq (CYVP) in Nunavik. The altimeter is set to the airport’s atmospheric pressure to reflect the correct height of the runways in relation to the aircraft. Near the airport, the autopilot is disconnected, and the approach is made manually and visually. The desired speed is around 135 knots for the final.
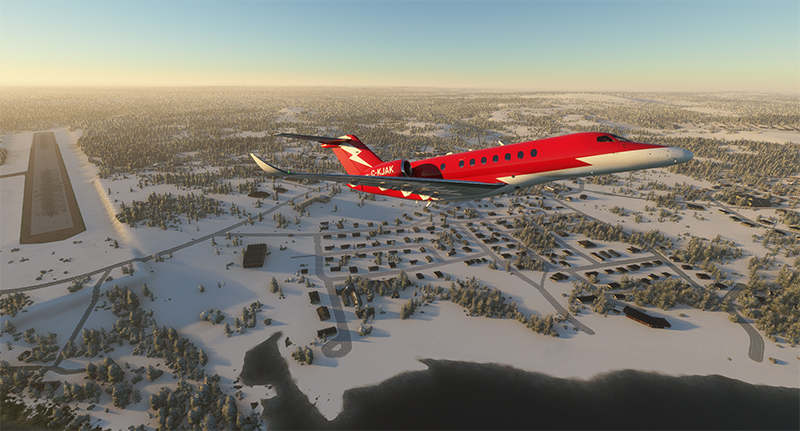

Above, the jet takes off from Kuujjuaq bound for Iqaluit (CYFB) on Baffin Island in Nunavut.
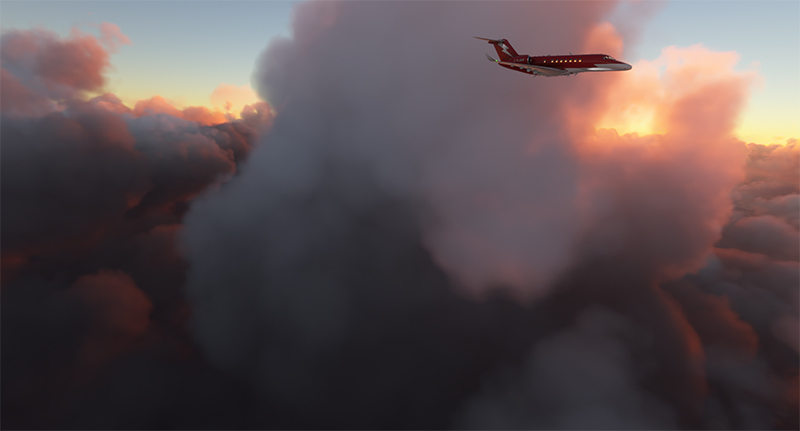

The setting sun illuminates the aircraft’s windows. The approach to Iqaluit has begun. The descent is gradual, so as not to cause discomfort to the virtual passengers…

Above, the aircraft is on final for runway 34 at Iqaluit (CYFB).
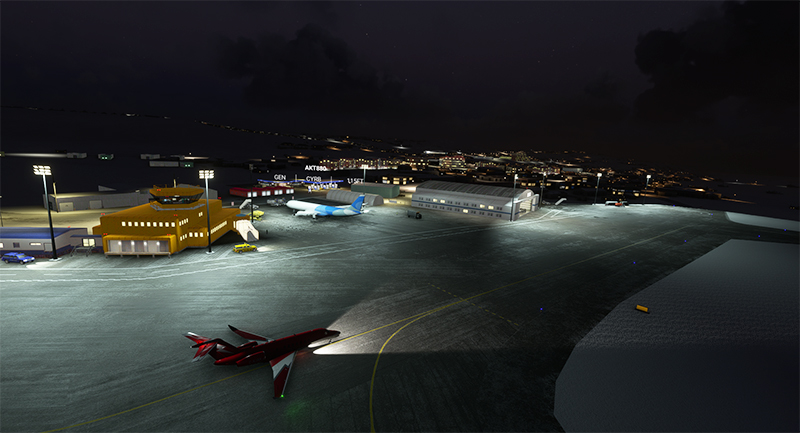

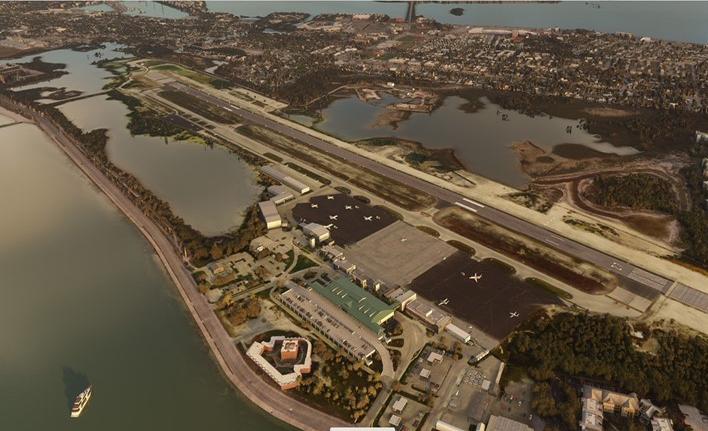
The first leg of our virtual flight around the world ends in Iqaluit, the airport where I worked for two and a half years as Flight Service Specialist (FSS) in the yellow tower on the left of the photo.
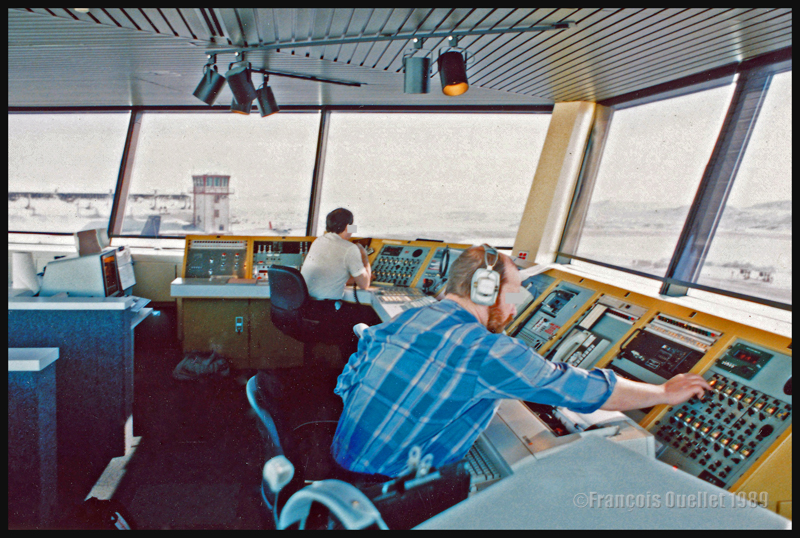

Above, a photo of the interior of the Flight Service Station at the time. One FSS worked on arrivals and departures at the airport, while the other handled transatlantic flights between Europe and mainly the western USA.
Click on the link for more flights around the world in flight simulation on my blog.













































































