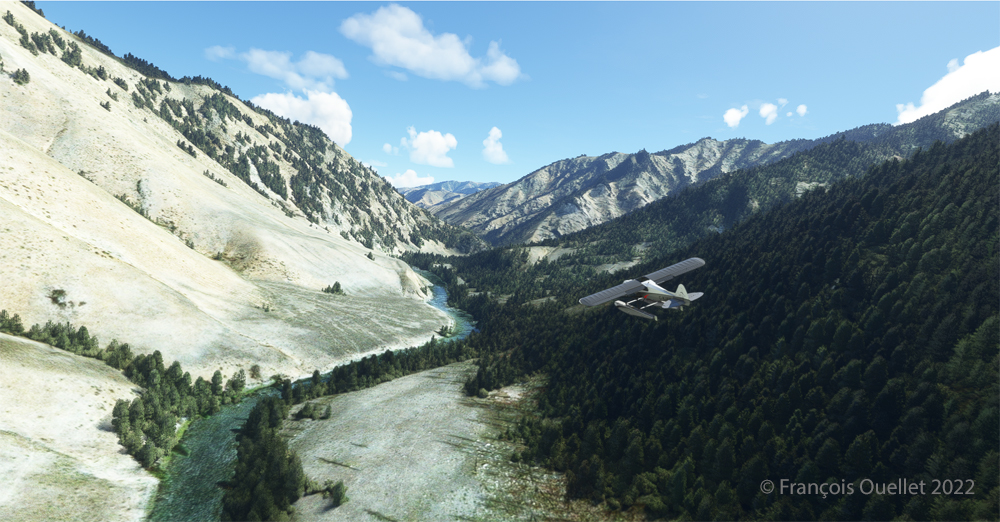
Today’s flight consists of two virtual short landings using the MSFS 2020 flight simulator (or as some call it, FS2020). We will be landing on Île d’Orléans and on the Battlefields Park.
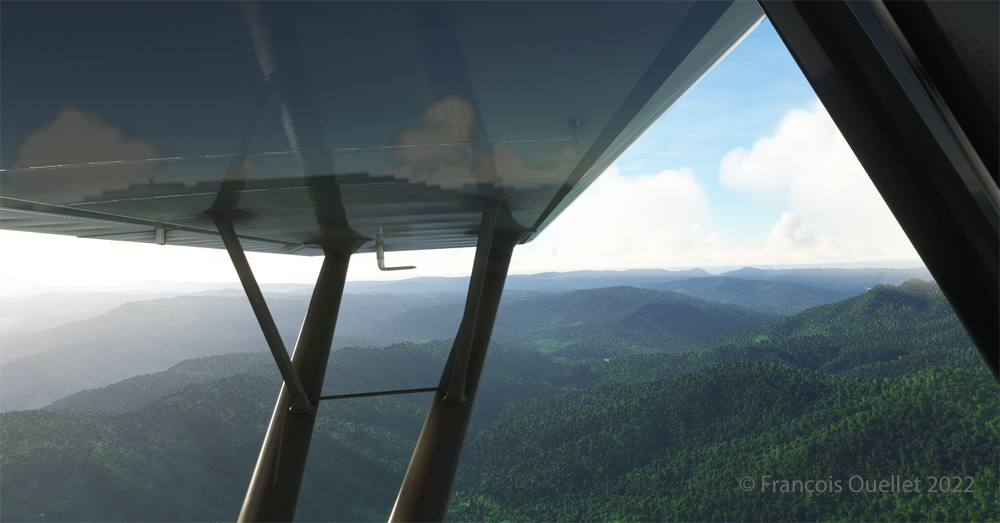
First of all, I admit that the Cessna 170B’s windows are dirty. For realism, the designer Carenado left a little dirt here and there to show the wear and tear of this very old aircraft.
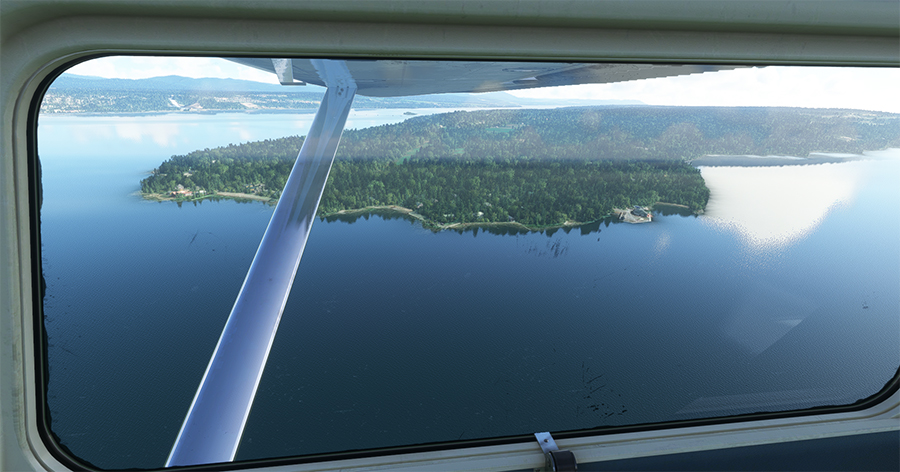
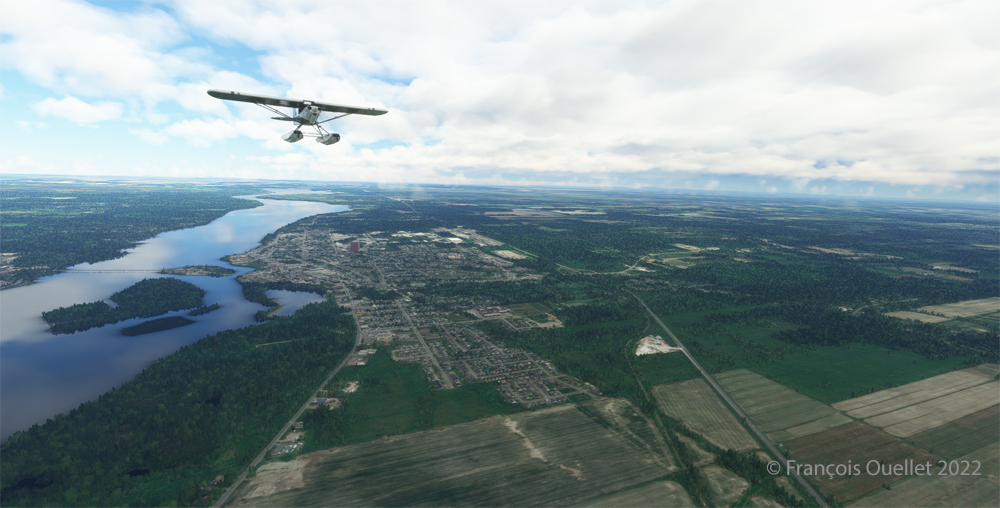
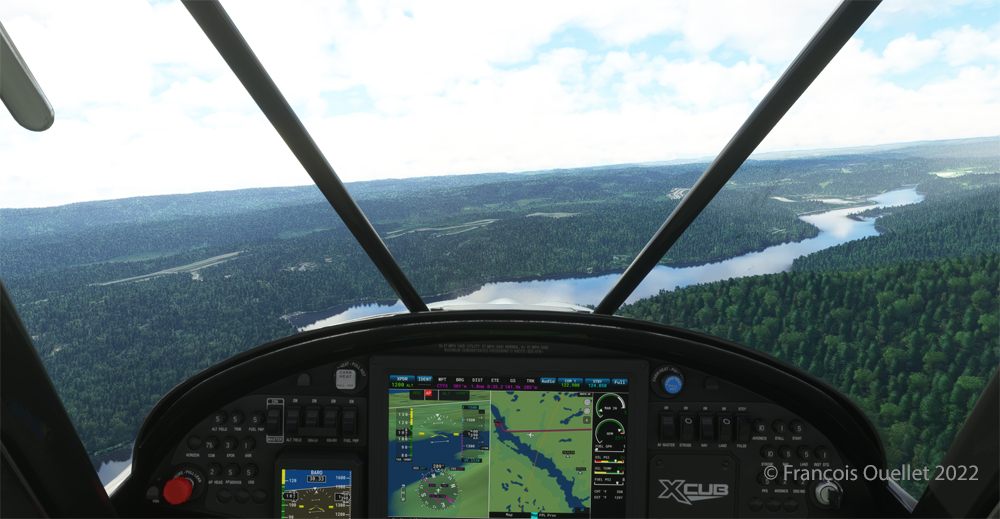
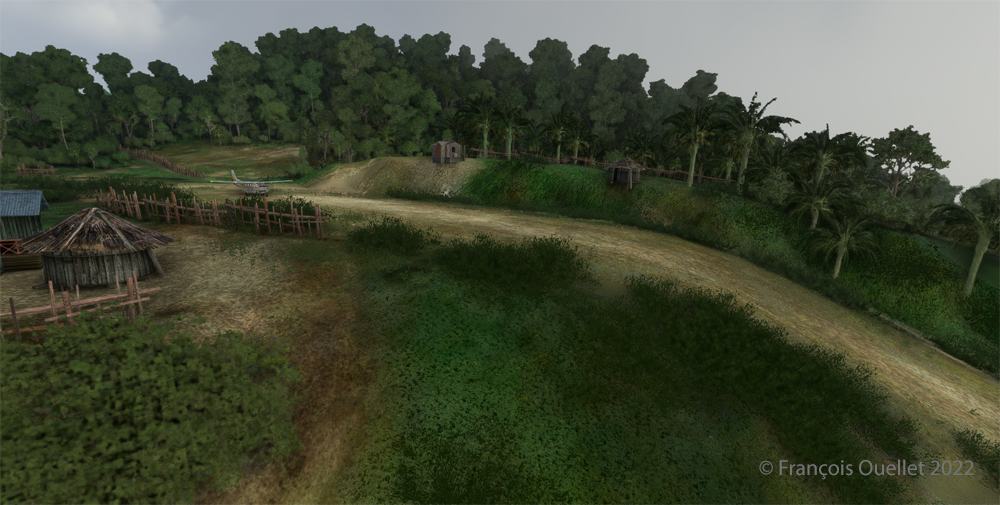
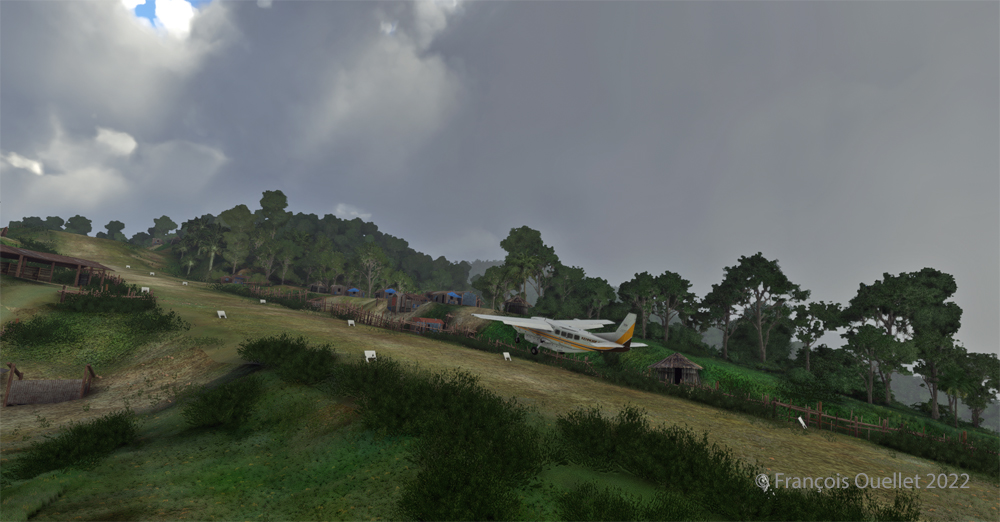
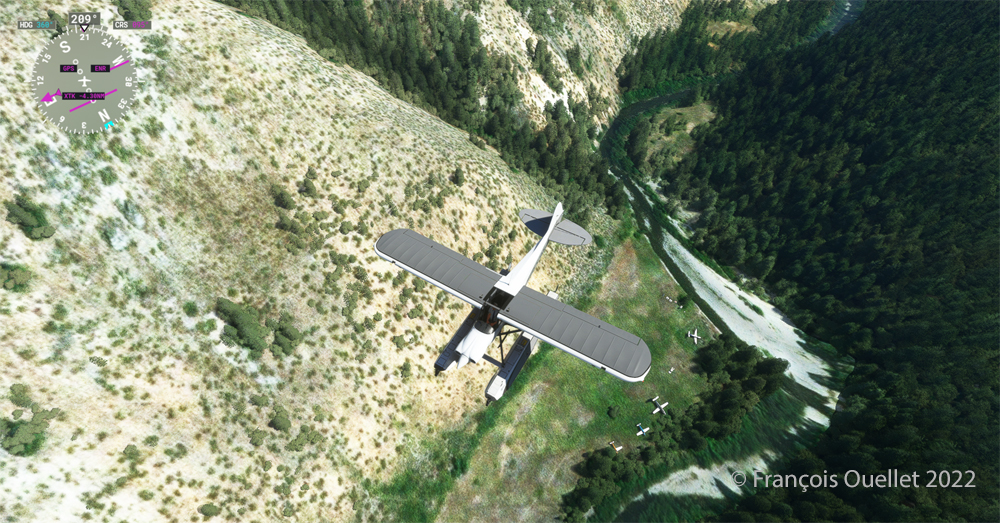
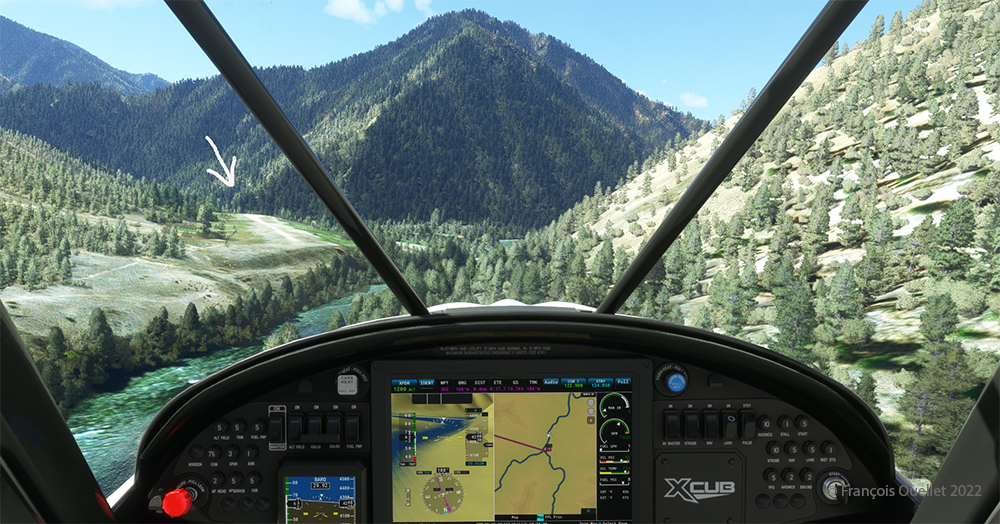
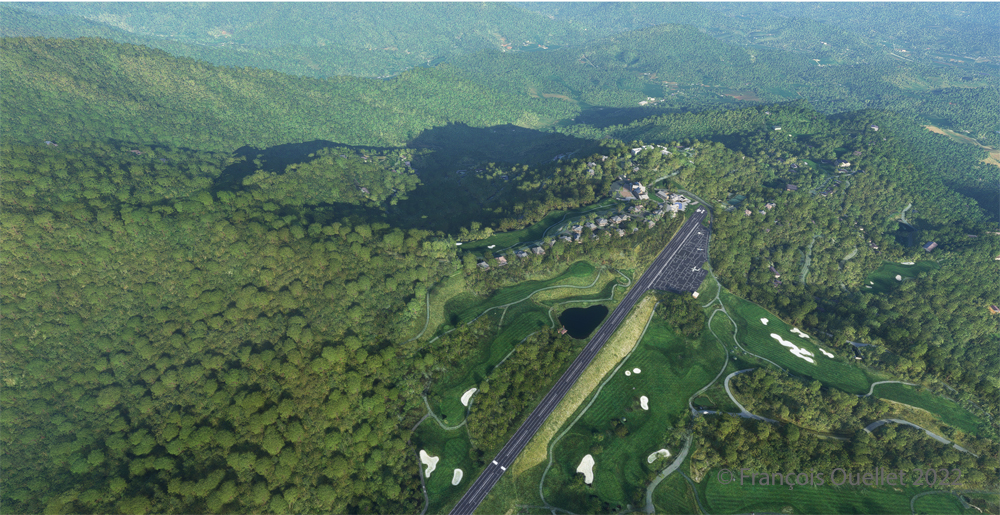
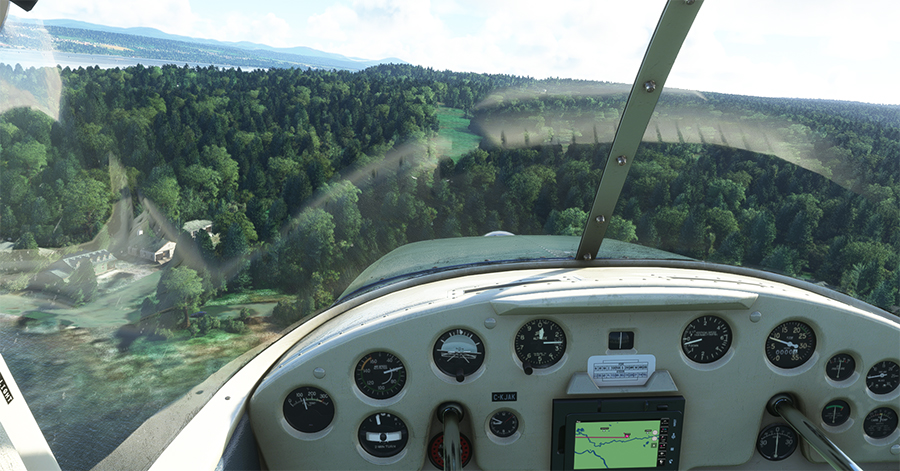
The picture above shows Île d’Orléans as seen from the Cessna. Since there is no landing strip but a golf club in the area, we will use the open fairways to land the aircraft. If there is a golfer on the course, I will open the window and yell, as is customary, “Fore!” (Falling Object Returning to Earth).

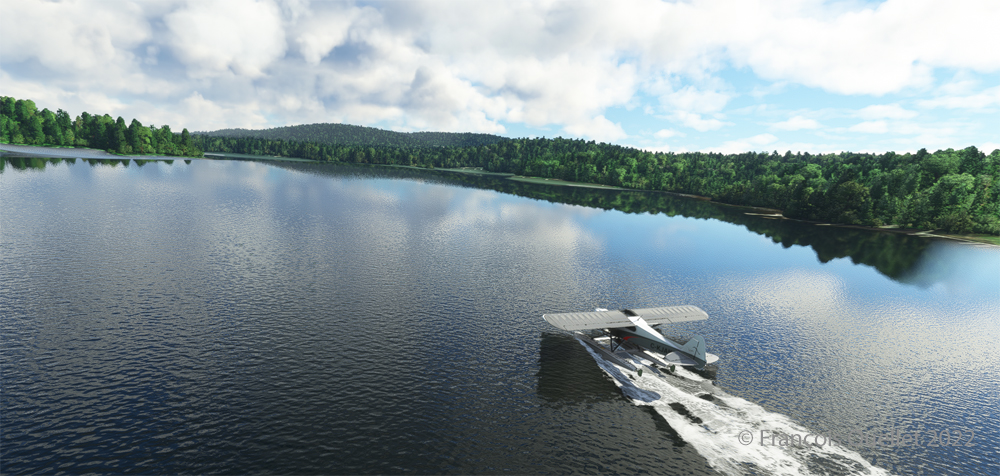
We are established on final for the small portion of open ground ahead. With 40 degrees of flaps, the stall speed is particularly low and the landing should not be too difficult.
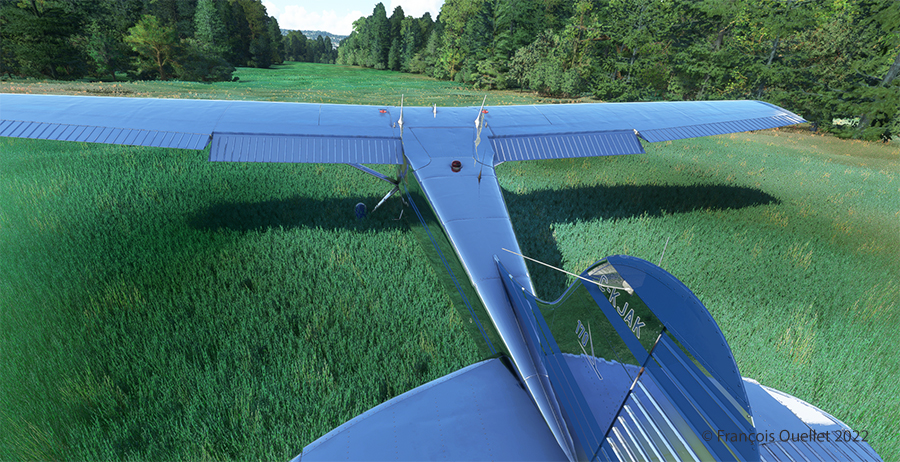

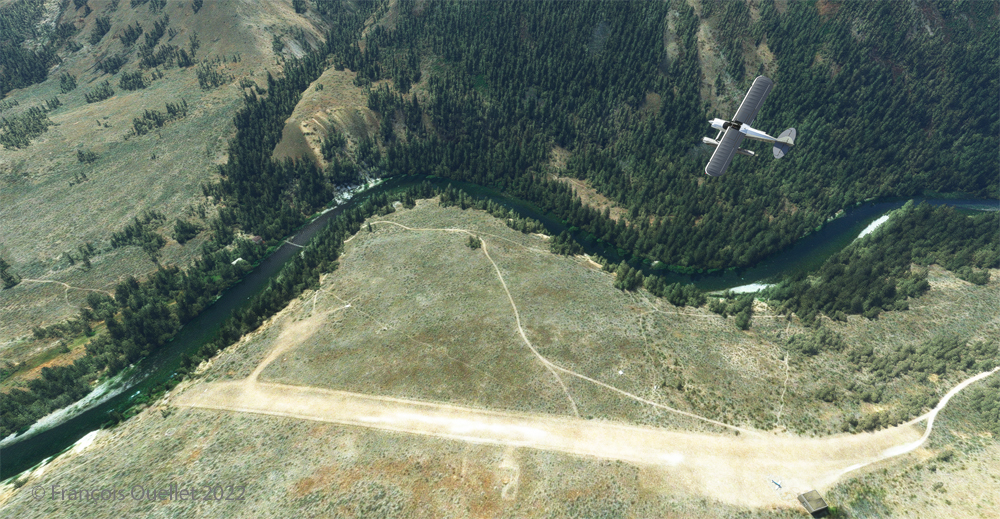
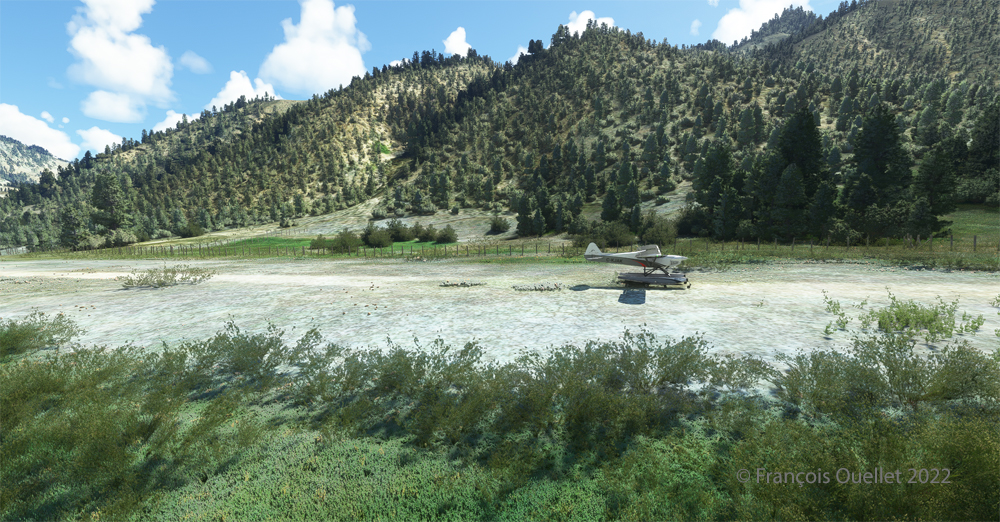
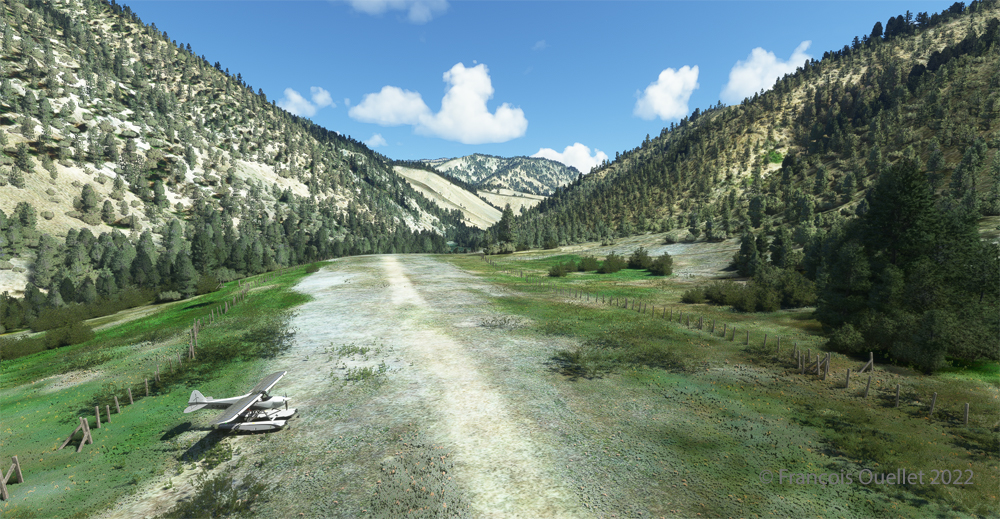
Although the available strip was not very wide, it was long enough for the landing, the taxiing and the maneuvering to turn the aircraft 180 degrees for its take-off to Quebec City.
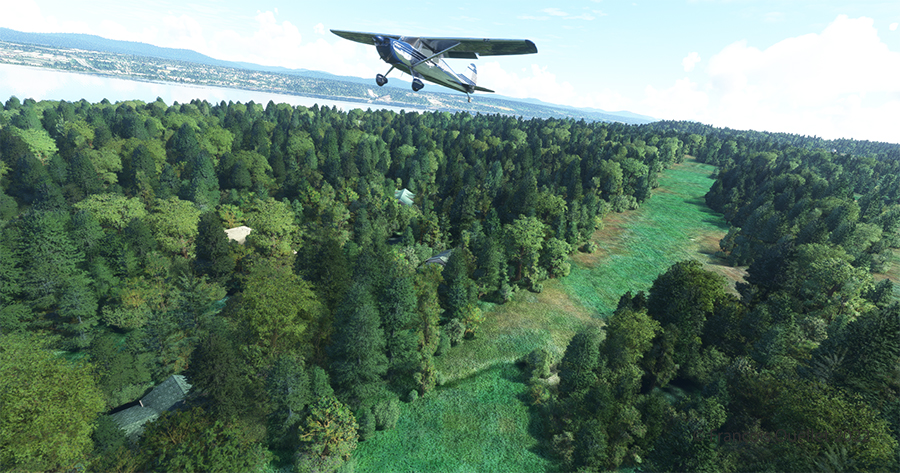

Back in the air, direction Quebec City. The take-off on soft ground requires about 20 degrees of flaps.
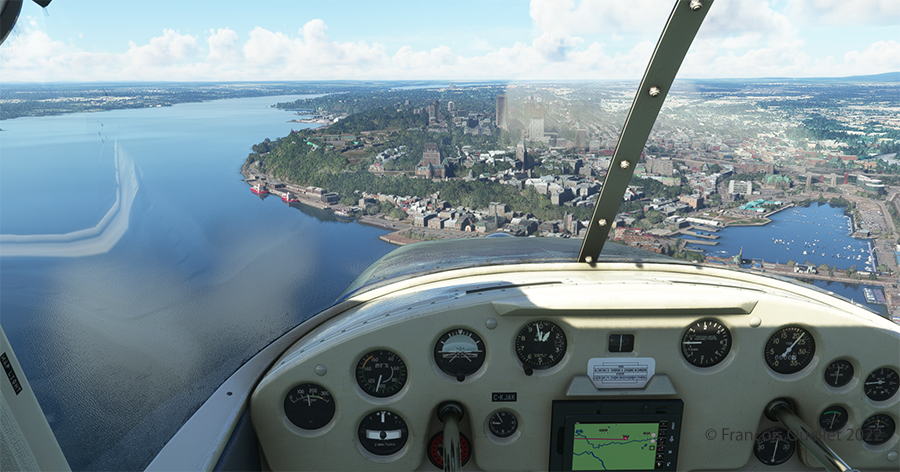

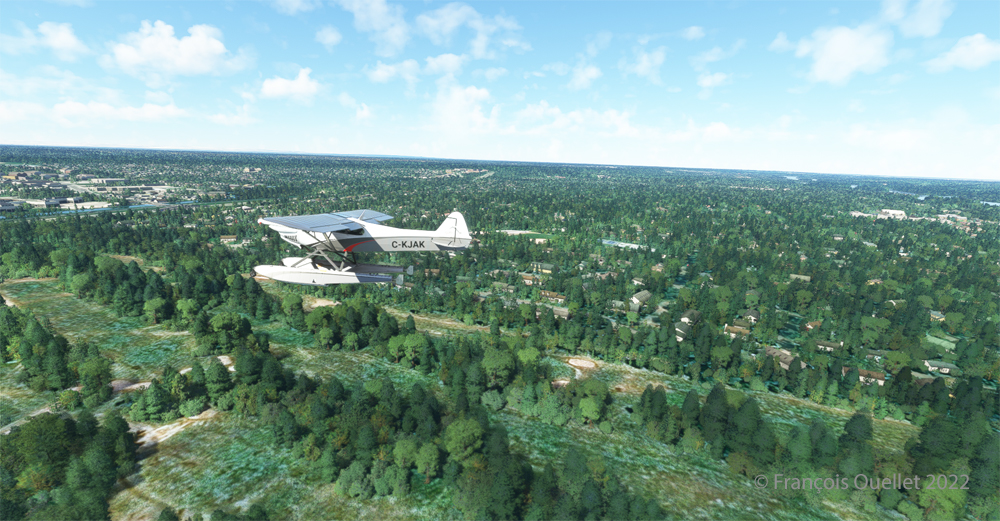
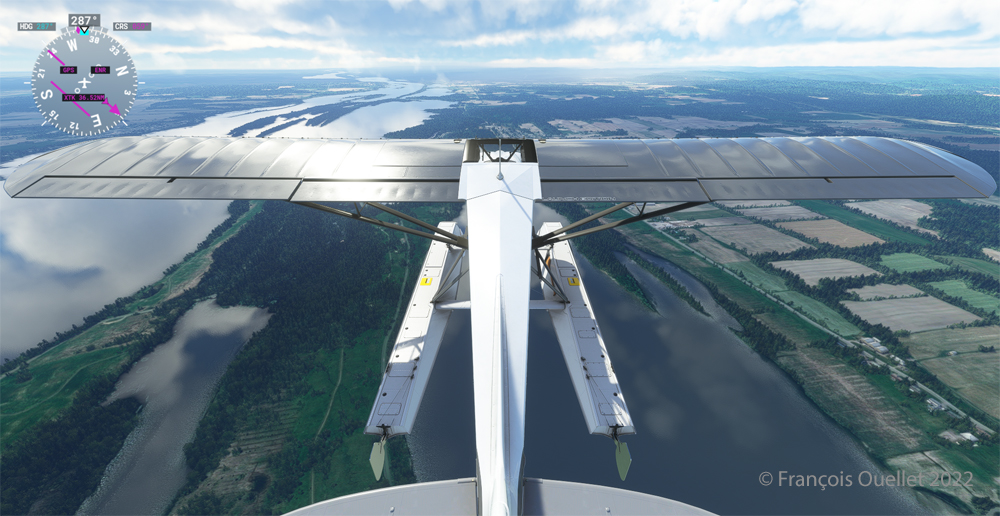
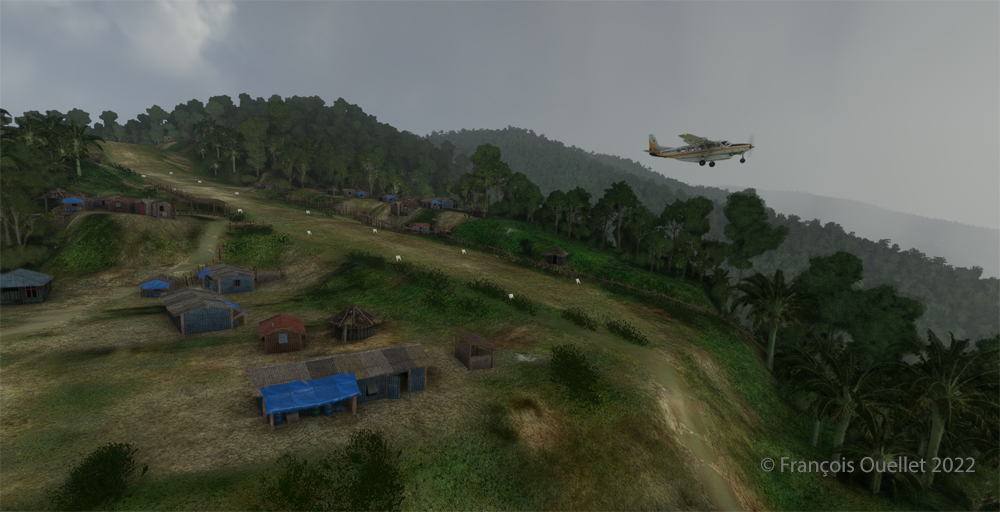
Quebec City is in sight. In the Cessna C-170B I flew in 1981 across Canada from St-Jean-sur-Richelieu to Edmonton, Alberta, there was no modern navigation aid installed on board as in the photo above, where the GPS helps the pilot find his way. The flight was flown using 14 VFR charts and nothing more. (If you are interested, click to read more about real-life flying stories on my blog).
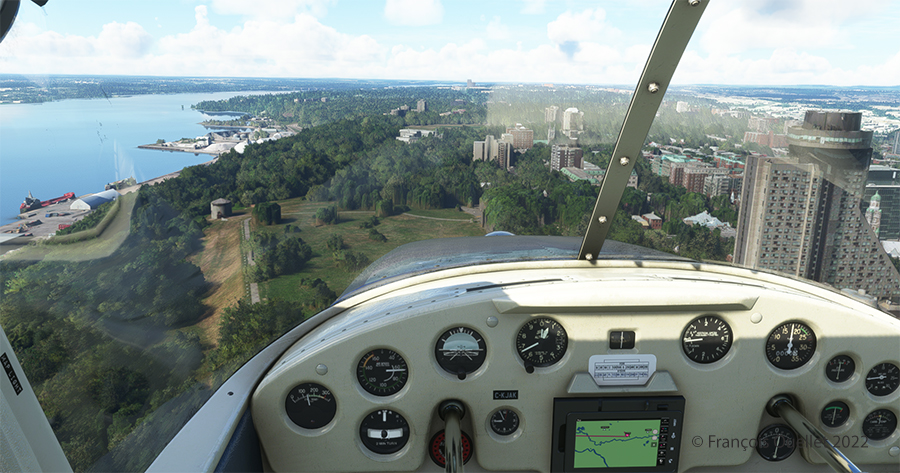

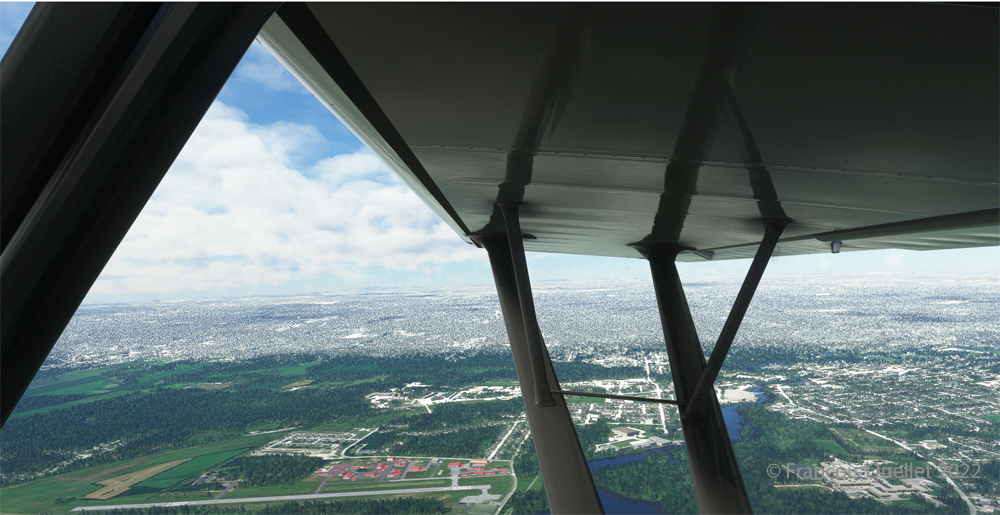
We are now above the Plains of Abraham. On the picture above, on the right, you can see the Hotel le Concorde and its revolving restaurant. We will possibly disturb the quiet atmosphere of the meal as we fly by…
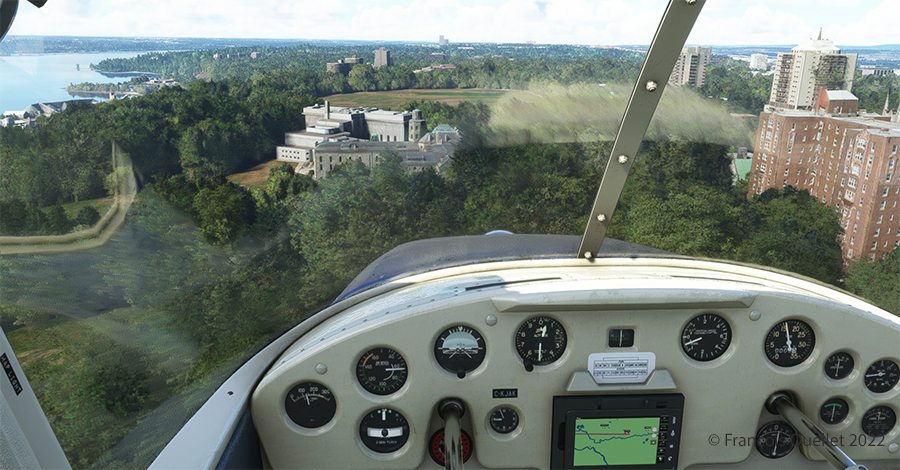

Above, straight ahead, the gray buildings represent a portion of the Musée National des Beaux-Arts de Québec (MNBAQ). A little further on is the open area of the Battlefields Park. In 1928, Lindbergh landed on that field to bring badly needed medicine for his friend Floyd Bennett. Can we normally land on the Battlefields Park, in the heart of Quebec City? Of course not. But that’s the beauty of a flight simulation; you can do whatever you want!
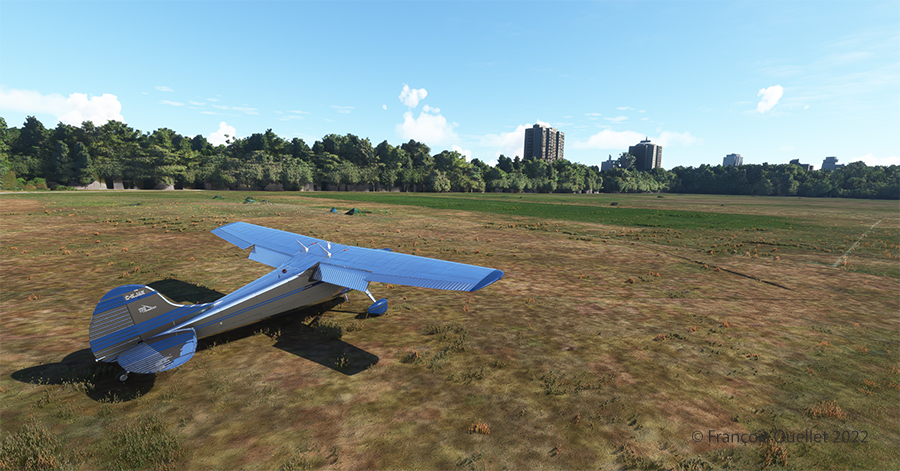

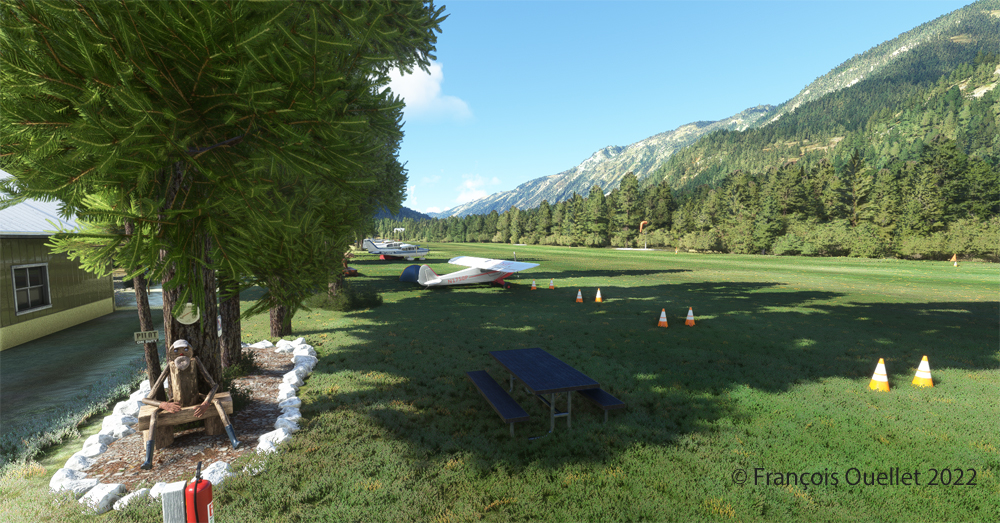
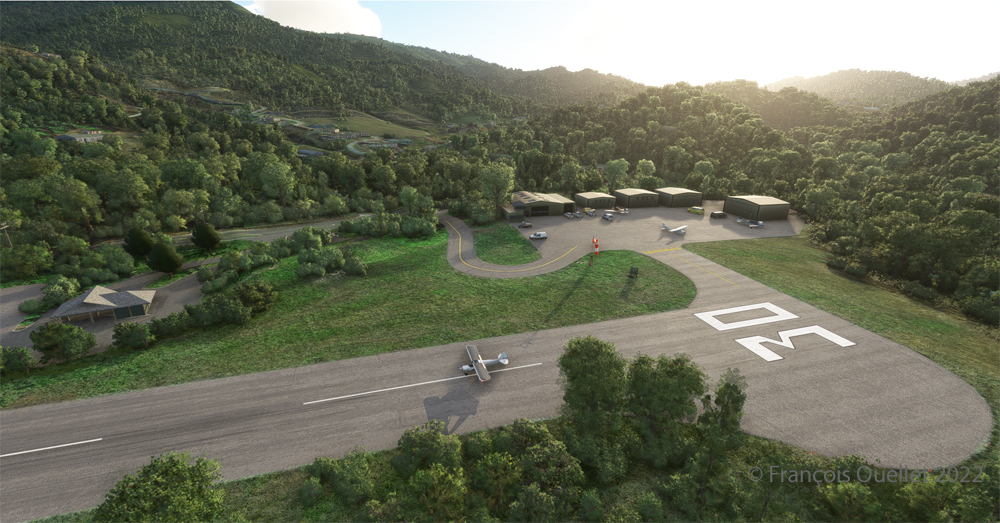
Once landed, the aircraft is allowed to decelerate gradually and then turned 180 degrees for the next takeoff. When winds are light, there is no need to worry about the direction of the takeoff.
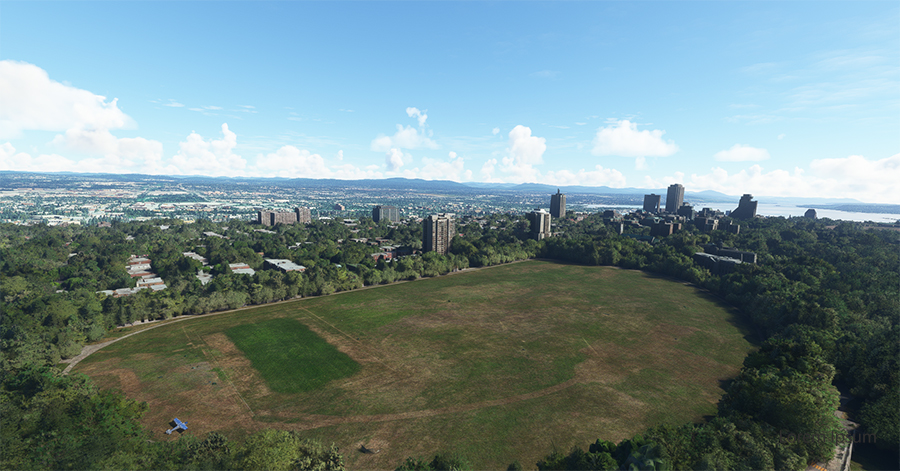

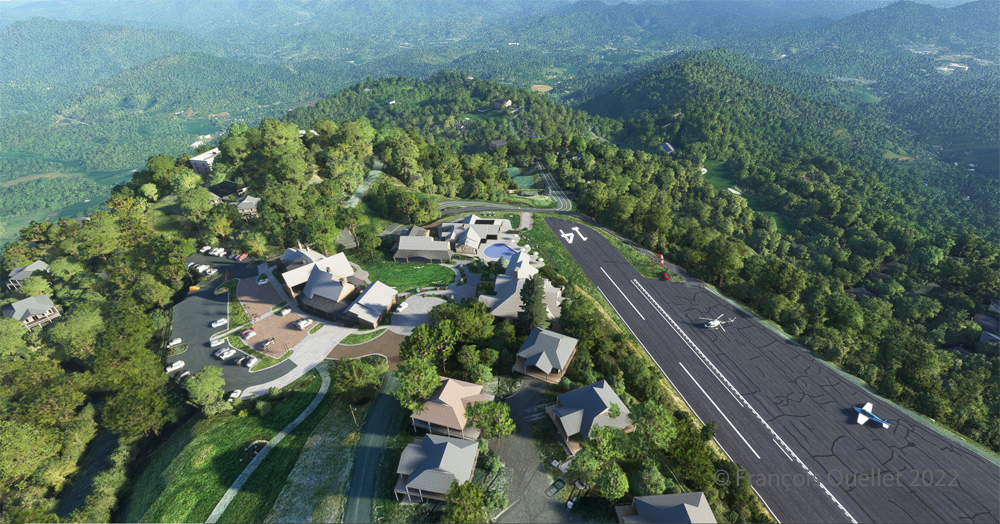
Above, an aerial view of the Battlefields Park, with the virtual Cessna C-170B ready to take off again.
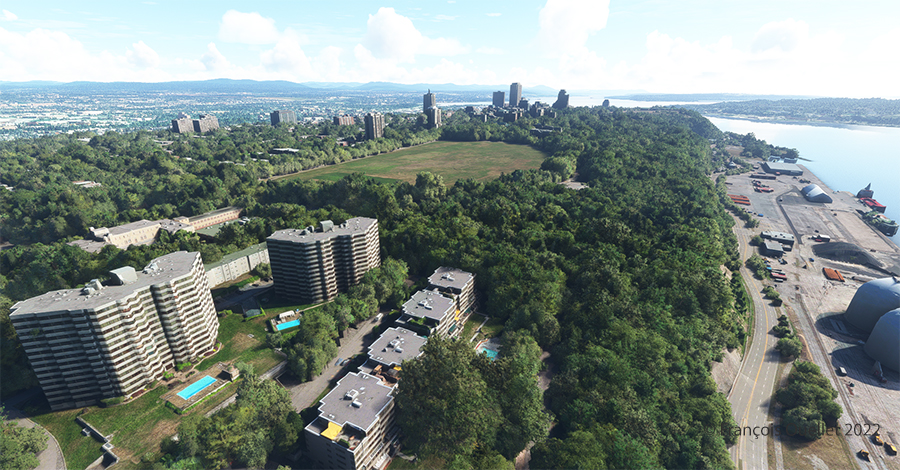

One last picture, this time with some additional buildings. The realism of the virtual scene with FS2020 is amazing!
I hope you enjoyed these two short flights. Whether you use the short landing technique for the Battlefields Park is really up to you, as there is enough space for a normal landing. But it is good to practice landing in the shortest distance possible. You never know when your engine will quit!
You can click on the following link for other challenging virtual flights on my blog.