Wanting to add an almost impossible flight in the “unhinged virtual flights” section of my web site, I tried a flight with the Blue Angels C-130 Hercules (Captain Sim) where the aircraft gradually lost all of its engines.

I am aware that the Blue Angels mechanics are real professionals, so I assumed that the engine failures were caused by an unknown reason.

The take-off was made without problem from the Canadian High River (CEN4) airport. This free airport was designed by Vlad Maly and is available through ORBX. The aircraft leaves the 4150 feet runway heading to the Coeur d’Alène airport (KCOE) in United States.
Eventually, the first engine stops. This does not cause a problem. The propeller is feathered and the gradual climbing continues.
The second engine stops. The pilot must forget the initial destination. Bonners Ferry (65S) becomes the alternate airport since the 4000×75 feet runway is good enough for the C-130.
The third engines gives way. A slow descent starts. Bonners Ferry is not very far. The airport is at an altitude of 2337 ft asl.
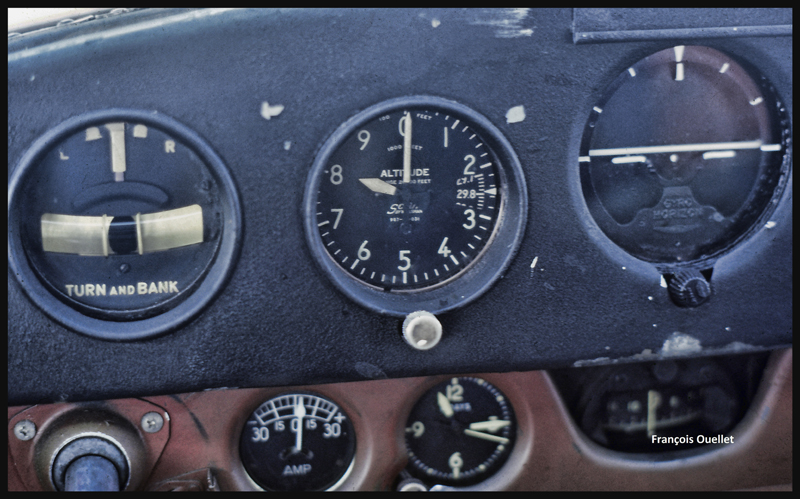
The aircraft is volontarily flown at a higher altitude than what would normally be requested for a normal approach, just in case the fourth engine stops. When three engines stop after the same refueling, the pilot has the right to think that what feeds the fourth engine can also cause problems.
The highest mountains are now behind the aircraft.
The Bonners Ferry (65S) runway is in sight.
The fourth engine stops. The flaps will not be functional for the landing.
From now on, the pilot should save the virtual flight a few times since it is possible that several trials will be necessary to glide sucessfully to the airport. This is the fun of virtual flight.
The C-130 Hercules has become a big glider. When the speed is maintained, the aircraft loses more 1000 feet per minute. It is easier to feel the aircraft’s inertia.
The wheels will be brought out only when necessary since the gear adds a lot of drag.
From the position indicated in the picture below, it is impossible to arrive to the airport in a straight line: the aircraft will glide over the airport. In the picture, the aircraft seems to be on a good path for landing, but it is an illusion caused by the wide-angle format chosen for the screen capture.
The aircraft is definitely too high. It is impossible to use the flaps to increase the rate of descent.

One must choose between 1) sideslips 2) a 360 degree turn to lose altitude or 3) multiple steep turns perpendicular to the runway to increase to distance to the airport.
What would you choose?
There is no universal method. The 360 degree turn is riskier but can prove efficient. An Airbus A330-200 flown by Quebecer Robert Piché that had lost all of its engines landed successfully in the Açores in 2001 after attempting a last minute 360 degree turn to lose altitude. But here, I did not believe there was enough altitude to safely complete the turn and reach the runway.
A few steep turns were made to extend to ride to the airport. Why steep turns? In order to avoid getting closer to the airport before an acceptable altitude was reached. This method helped keep an eye on the runway at all times to verify if the slope to the airport was still acceptable.
I tried the three methods, always starting from the same saved flight (photo 10). After several sideslips, the aircraft was always approaching the airport too quickly. There was not enough time to lose altitude. The final speed always happened to be too high to stop a C-130 without flaps or thrust reversers.
The 360 degree turn, be it right or left, with different angles and a reasonable speed, always incurred a loss of altitude that brought the aircraft 200 to 300 feet short of the threshold.
Finally, after a few steep turns, the aircraft was positioned on final with the appropriate speed and altitude.

A few last seconds adjustments, to reposition the aircraft in the center of the runway.
At 140 kts, but without any reverse thrust, the whole runway should be necessary to stop the aircraft.
The landing was smooth and the aircraft stopped short of the threshold.
For an unknown reason, the anemometer was still indicating a 10 kts airspeed, even when the aircraft had stopped.
Try such a flight in the virtual mode. The worst that can happen is that you have fun!
For more near impossible flights, head to: