« Passer par le Nord » (Northern Sea Route), by Isabelle Autissier and Érik Orsenna, is an essential book for the reader who wishes to learn more about the profound transformations brought on by global warming, with regards to geopolitical, economic and ecological issues in the Arctic.
The book is at the same time a lesson in geography, history, politics, ecology and economy. It will certainly captivate those who are interested in maritime traffic and the development of new maritime routes, as well as the race towards the appropriation and exploitation of the immense oil and gas resources of the North.
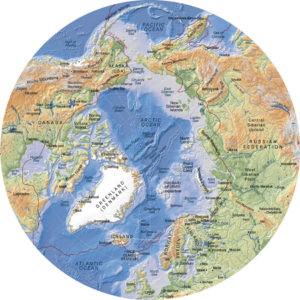
In order to sustain the reader’s interest, several maps are included in the book. They are very useful when comes the time to better understand the history and different uses, past and present, of the seas, islands and territories like: Kara Sea, Barents Sea, Laptev Sea, Franz Josef Land, Novaya Zemlya, Aleutian Islands, New Siberian Islands, North Land, Wrangel, Bering Strait, Svalbard, Spitzberg, Oslo, Tromsö, Kirkenes, Murmansk, etc.
Some of the seaways of Russia, which are among the longest in the world, are equally presented: Ob, Yenisei, Lena and Kolyma.
Numerous geographical maps are available at the following site : http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/polar.html
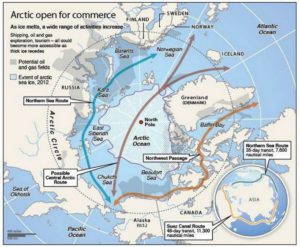
The numbers talk for themselves: to go from Rotterdam to Yokohama, a ship must travel 20,600 kilometers when passing through the Suez Canal. Only 12,800 kilometers are needed when using the northeast passage along the Siberian coast and 11,800 kilometers when traveling across the pole in the absence of ice during summer (this new transpolar route could be usable as soon as 2025). The need of resources by China and India, associated with melting ice in the poles, are rapidly taking Siberia out of its isolation.
Important people
The reader will certainly be interested by the information on the people who played a significant role in the discovery and exploitation of seas, islands and lands bordering the Northeast maritime route. Here are few of those names: the Viking Otar, Willem Barents, Simon Dejnev, Vitus Bering, Peter the Great, Alexander Baranov, Ivan Veniaminov, Adolf Erik Nordenskjöld, Ada Blackjack, etc.
The first northern crossing from the Atlantic to the Pacific belongs to a Swedish named Adolf Erik Nordenskjöld in 1879. Thirty-six years (1915) were needed to witness the second complete crossing, this time by Russian icebreakers under the command of Boris Vilkitski.
The importance of icebreakers
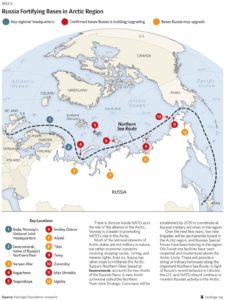
Icebreakers are extremely important for Russia, so much for protecting its recognized sovereignty and defending its new territorial claims than for economic reasons (insure the usability of the Northeast Passage and the continuous exploitation of the oil and gas resources along the Siberian coast).
The United States must also build icebreakers, so much for geopolitical and economic reasons than to insure the protection of a growing number of cruise ships that are about to use the narrow and risky channels of the Arctic.
Collaboration and obstacles in the Barents Sea
An obvious collaboration exists between Russia and Norway with regards to fishing in the Barents Sea and in the south of Svalbard, a sector rapidly becoming more strategic with the northern migration of several fish species caused by the climatic changes. Ecosystems are nonetheless in danger due to the rapidly warming waters and insufficient time to adapt.
What are the obstacles presented by the Barents Sea towards tankers, ships and platforms? First the fog, which can last for weeks, than the “lows” which destroy vessels and twist superstructures. Finally, freezing spray adds excessive weight and freezes every crank on ships and platforms. In the event of an accident caused by oil or gas exploitation, the extreme meteorological conditions will present very important challenges.
One note on Siberia
The exploitation of mineral resources in Siberia was initially made possible, under Lenin, through work camps (gulags), since there were no volunteers ready to exile themselves in that hostile region.
The authors suggest, for whoever is interested in Siberia, the soon to be published book by Éric Hoesli. He has already published, in 2006, a very well documented book on the Caucasus: À la conquête du Caucase.
Oslo: Tschudi and Aker Solutions
The authors present two Norwegian companies based in Oslo which deal with logistics at sea: TSCHUDI and Aker Solutions.
Shtokman and Yuzhno-Tambeyskoye natural gas reserves
The reader will certainly appreciate the chapter on the “eldorados glacés” (iced eldorados) which develops on the Shtockman and Yuzhno-Tambeyskoyenatural gas reserves fields (the latter holds 25% of the world reserve of natural gas). There are numerous challenges with regards to the exploitation of those fields: investments of twenty billion dollars, a necessary alliance between Russia, France (TOTAL) and China (CNPC), gigantic infrastructures to be built, the stabilization of all installations using thousands of posts, a constant fight against ice, the construction of thirty tankers (among them sixteen icebreakers), and the obligation to use the Northern maritime route.
Global warming
The book covers at length the accumulated effects of military, industrial and commercial activities on animal life and the environment. The fragility of the Arctic is well demonstrated. The reader will be surprised by the extent of nuclear wastes spread around the Novaya Zemlya.
The global warming favors the migration of species northward, an increase in the number of fishing vessels in the Arctic and political tensions between nations related to the ownership of the zone located between 12 and 200 miles along the different coasts. The native species are losing ground to the profit of the invasive species.
“[My translation] The diminishing polar ice will favor an increase in the number of ships in the Arctic with the added risk of collisions and the emission of all kind of noises that disrupt animals and prevent them from feeding correctly and communicate properly between them or with their offspring. Seismic tests or low-frequency sonars used by fishermen and militaries are particularly devastating.” (p.203)
“With few exceptions (Norway, Japan, Iceland), the moratorium on whale hunting is respected. The official predation by Inuit and the Russian poaching are limited.” (p.203)
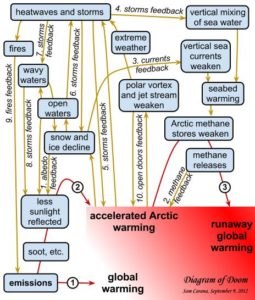
Increase in extreme weather events
“[My translation] The diminishing pack ice will act on the oceanic currents, but also on the atmosphere by slowing down the higher jet streams. This phenomenon will favor an increase in extreme [weather] events (cold spells or heat waves, droughts or floods) at our mid-latitudes.”(p.219)
Response time when faced with an ecological disaster in the Arctic
The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (USA) “[my translation] estimates that 61 000 barrels [of oil] would spill in the sea every day if a well exploded. The Shell Company indicates that it would need thirty-eight days to drill a relief well while it needed eighty-five in the Gulf of Mexico, infinitely more accessible and less dangerous. Admitting that it would show the same celerity as for Deepwater Horizon , which in itself would be a feat, more than 800 000 tons of oil would spill in the Arctic.
More likely, operating conditions in ice, fog and storms would prevent the realization of the work within only one summer. Once the polar night would set, a decision to let the well spill all winter would have to be taken, if not for many years in a row.” (p.229)
Methane
“[My translation] Methane has a greenhouse effect that is twenty-three time superior to that of the CO2, that is already presented as our worst enemy” (p.216)
“In the Laptev Sea, what looks like real fountains of several hundred of meters in diameter spew out methane. One can see the sea boil like if it was in a gigantic cauldron. 80% of surface waters and 50% of deep waters present methane concentrations varying from 8 to … 1 400 times the oceanic average!”(p.216)
Mammoth’s tusks poaching
There is a short passage in the book on the poaching of mammoth’s tusks buried in the ground on Liakhov Island. The operation is financed by Mafiosi. The tusks are carved then resold to Chinese collectors for a very good profit.
Global warming, and the thaw it provokes in Siberia, would indirectly protect the African elephant by allowing access to mammoth’s tusks. The new and important stock of ivory in Siberia drives the price down by increasing the offer, thus making the African elephant’s tusks less interesting financially.
Some names to remember
The Port of Kirkenes, in Norway, is one of the main ports of the new northern sea route. It has an ideal geographical position and its harbour is protected against storms. The city favors the development of the port. The efficiency of Norwegian employees is recognized. The Norwegians are used to deal with Russians, their immediate neighbours.
Murmansk, in Russia, is also expected to benefit from global warming. There are already dozens of mines in exploitation, with several of those mines producing rare earths which are vital for modern technology applications.
In the Arctic, the disappearance of the summer ice pack is expected between 2020 and 2030. The Northeast Passage could be accessible beyond the EEZ 200 miles, “which will favor Iceland “which could become a transport hub between America and Europe.”(p.218). “And it is said that some Beijing investors would be ready to offer 5 billion dollars to take control of the future Port of Reykjavik, the one that aims to be the hub of the North.” (p.245)
The Arctic Council
For a long time now, the Arctic has been a strategic area where numerous countries, among them few superpowers, claim an important part of the territory and resources. With the acceleration of the melting process, things get even more complicated.
In 1996, the Arctic Council was created to ease communications and reduce political tensions between the countries pretending to part of the Arctic territory and resources. These countries include Canada, Denmark, United States, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden and Russia. Associations of indigenous population are also part of the group, but as “permanent members”.
Militarization of the North
The Cold War between Russia and United States forced the construction of the DEW line by Americans and Canadians, a line that was eventually replaced by the North Warning System.
Today, the militarization of the area still goes on: “[my translation] Russia multiplies the signs and acts of militarization in the zone. Military exercises (parachuting, air patrols), reconstruction of installations in all of the islands (Wrangel, New Siberian, Novaya Zemlya, Franz Josef Land), orders of numerous ships among them new generation submarines (attack submarines and missile launchers), a complete program for the upgrading of the Boulava missiles … The [Northern Fleet] underwater base, near Murmansk (Severomorsk), seems to be in a state of complete reactivation.”(p.238)
The transpolar maritime route
The Northeast Passage maritime route along the Siberian coast will be favored until the ice pack has melted at the pole (expected for 2025 instead of 2060 initially forecasted). So, in 2025, a new transpolar maritime route will be available to ship-owners. They will then be able to decide if they avoid the Siberian coast and the associated administrative hassle while they save an additional one thousand kilometers for a route from Rotterdam to Yokohama.
For more articles on geopolitics on my web site, click on the following link : Geopolitics
Title: Passer par le Nord – La nouvelle route maritime
Authors: Isabelle Autissier and Érik Orsenna
Editions: Paulsen
©2014
ISBN: 978-2-916-552-35-4