(Precedent story: carrying a .357 Magnum to Iqaluit)

Before retelling some of the events that happened while I was working at the Transport Canada flight service station in Iqaluit, in the Nunavut (1989-1991), it is mandatory to present few important dates that will allow the reader to understand why the airport was initially an American military base.
1938. Hitler’s ambitions are such that Roosevelt deemed necessary to announce the following: “I give you assurance that the people of the United States will not stand idly by if domination of Canadian soil is threatened by any other empire ».
1939. Beginning of discussions between Canada and United States with regards to joint defense of the North American continent.
1940. Great-Britain was at risk of losing the war against a Germany that was progressing rapidly in its conquest of the European soil. When Denmark was defeated in autumn 1940, fear grew that the Germans would progress westward and establish operational military bases on the newly acquired territories.
Greenland belonging to a defeated Denmark, Germans would be using it to get closer to Canada. At the time, Greenland was the sole commercial source of cryolite, an essential component of aluminum used in aircraft production.
There was also a province which was not part of Canada in 1940 and which presented a strategic interest for an enemy in its war against Canada and United States: Newfoundland and Labrador.
In order for the war not to be fought directly on the North American territory, one had to keep the Germans busy in Europe. It therefore meant that Great-Britain must not be defeated.
1941. Ships carrying short range fighting aircrafts from America to Europe were regularly attacked and sunk by U-boats. It was imperative to change the route. Canadians and Americans were looking for the best sites that could accommodate the construction of runways allowing short range military aircrafts to fly up to Prestwick, Scotland.
This new route was called “Crimson Route” and the stopovers were Goose Bay in Labrador, Fort Chimo (Kuujjuaq) in Quebec, Frobisher Bay (Iqaluit), on Baffin Island in the Nunavut as well as three sites in Greenland (Narsarsuaq, Angmagssalik and Sondre Stromfjord (Kangerlussuaq). The Frobisher Bay coded name became “Crystal Two” base.
1941-42. Germans established the first inhabited weather bases on the Greenland coast in order to facilitate U-Boats operations across the North Atlantic. When those sites were discovered, they were destroyed by American commandos.
1942. U-Boats entered the St-Lawrence seaway and sank Canadian ships.
1942. The site initially chosen to establish the Frobisher Bay airport (the Crystal Two base) was Cromwell Island, located 20 miles south-west of today’s actual site for Iqaluit. This was until a new site was discovered (today’s site) that favored the construction of longer runways and allowed the beaching of flatboats loaded with cargo during the summer period.
A ships convoy carrying thousands of tons of cargo planned for the construction of the Frobisher Bay base arrived at destination. This convoy was nonetheless attacked by the U-517 U-Boat and the cargo-ship Chatham, carrying 6000 tons of material destined for Crystal One and Crystal Two bases was sank.
1943. An German automated weather station was built at Martin Bay, in Labrador, to facilitate the U-Boats operations. This weather station is now in permanent exhibition at the war museum in Ottawa. Pictures have been found were we can see smiling but armed German soldiers taking the pose near the automated weather station. Canada accidently learned about the existence of that weather station in 1980.
Many German officers and soldiers who were captured in Europe were sent abroad while waiting for the end of the war. My grandparents, who owned a farm in St-Ignace, Quebec, became responsible, over time, for one German officer and two soldiers. They had only good comments on the behavior and desire of the prisoners to help on the farm.
1943. Both Frobisher Bay runways were now operational, although without being totally completed. The engineers did not have the knowledge of the Russians when it came to maintaining airport runways in the Arctic. Damages caused by permafrost were significant and the runways necessitated a lot of maintenance. The water present under the runways would sometimes surface suddenly and create five meter deep holes. Those runways needed a constant effort to remain usable.
The first runway to be built was eventually abandoned due to a wrong evaluation of the prevailing winds and the dangers associated with the surrounding elevated terrain. Today only remains the runway that we know in Iqaluit, although extended to 9000 feet. The year 1943 recorded 323 aircraft arrivals, of which only a small number made the complete trip to Europe.
1944. War took a new turn. The newly developed long range radars, allied to advanced technology in the detection and attack of submarines, radically diminished the U-Boats threat in North Atlantic. The “Crimson Route” airports were suddenly losing their pertinence. The Canadian government, worried about the massive presence of Americans in the Canadian Arctic, bought the airports from the American government.
1950. Canadians officially took control of the Frobisher Bay airport, but authorized an American presence since this airport had a new strategic importance in the cold war that followed Second World War. The weather station and runway maintenance were taken care of by American forces.
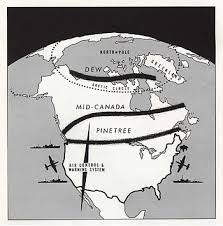
1951-53. A radar station was built on a hill northeast of runway 17-35. This station completed what was then known as the Pinetree line. This line was made of several long range surveillance radar stations; it covered all of southern Canada and gradually curved towards the north to end up in Frobisher Bay. All those stations were inhabited and could order interceptions at all times against potential enemy forces, by means of jet aircrafts.

1955. Americans received the authorization from Canada to build a SAC [Strategic Air Command] military base where numerous KC-97 tankers were stationed in support of B-47 bombers operations carrying nuclear armament. The base was built in 1958 and, until the end of its operations in 1963, parking space was occupied by at least seven KC-97. The SAC base was not needed anymore after the new Boeing B-52 bombers and KC-135 tankers were developed.
A French-Canadian military from Quebec at work in Frobisher Bay

My uncle Gaston Gagnon was part of the French-Canadian military staff who was in service in Frobisher Bay. He volunteered for service during the Second World War (1939-1945).

He worked in the communication field during the Cold War and, after he died in 2016, I received some pictures that were taken in 1955 in Frobisher Bay. Those photos also witness of the American presence in Frobisher Bay.

1960. The runway was extended from 6000 to 9000 feet.
1961. The Frobisher Bay radar station, part of the Pinetree line, was closed but the Polevault station remained in activity.
1963. Americans left Frobisher Bay and gave control of the Polevault station to the DOT [Department of Transport], an older designation of Transport Canada.
1964. The radio operator, and later flight service specialist (FSS) Georges McDougall, arrived in Frobisher Bay. All the village inhabitants eventually got to know Georges since he provided air traffic services there for at least thirty-seven years, seven days a week, on shifts work. He progressively became a privileged witness of all the unusual events to happen in the village and at the airport.
Below is a picture of the old DOT hangar and tower.
1987. Frobisher Bay was renamed Iqaluit.
1989. Stacey Campbell wrote an article in News North that she titled: “Military Jets Fill the Arctic Skies”. She explained that NORAD (North American Air Defence) regularly held exercises aimed at testing the capacity of Canada’s new radar defense system to detect potential enemies approaching from the north.
The interviewed military officer told Stacey that CF-18 fighter jets, tankers and B-52 bombers, among other types, would be part of the operation. The CF-18’s would temporarily be stationed in Iqaluit, on Baffin Island, and Inuvik for the duration of the exercise. Other types of aircrafts were also involved in that annual test, like the F-15, T-33 and possibly the AWAC although the latter did not land in Iqaluit.
The local Transport Canada flight service specialists (FSS) had to deal with the tight operating schedule provided by a military officer as well as integrate the daily arrivals and departures of private and commercial aircrafts.
At the time, the most useful taxiway, one which was located near the end of runway 35, could not be used since the terrain was too soft. All the aircrafts using runway 35 were forced to backtrack that runway before it could be cleared for other incoming or departing aircrafts. The additional time required for that procedure sometimes gave headaches to the military officer sitting by our side.
I remember that the military officer in charge of the mission told us: “If the jets cannot takeoff within the next minute, the mission will be aborted”. It just happened that during the tight window within which the CF-18’s had to be airborne that day, there were many commercial aircrafts like the Avro 748, Twin Otter, Boeing 727 and 737 and other executive aircrafts operating around Iqaluit. There was always a way to please everybody and the military exercise ended the way it was initially planned.
This was a period much appreciated by the flight service specialists (FSS) since, for one week during the year, our operations changed radically: we had to respect the imperative needs related to the military exercise as well as continue to provide regular air traffic services.
It was brought to our attention, for having discussed with many pilots involved in the exercise that military forces were kind enough to offer, through our Transport Canada manager, few posters signed by pilots of squadrons involved in the “Amalgam Chief” exercise. Although the manager never deemed necessary to show his staff even one of those posters, I appreciated the gesture from the pilots.
1993. In order to replace a DEW line that had become obsolete, Canadians and Americans jointly built a new base that would now be used for logistical support for the new North Warning System.
2006. Extreme cold tests were held in Iqaluit by Airbus for the A-380, the biggest passenger aircraft in the world.
2014. Extreme cold tests were held by Airbus for its new A-350 XWB.
2015. Canada was the host of the Arctic Council Ministerial Meeting in Iqaluit. The Council is composed of the following countries: Canada, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia and United States. Joining the meeting were senior representatives of indigenous organisations holding the status of permanent participants.
- Dassault completes several cold-soak trials in Iqaluit for its Falcon 6X
- Pope Francis visits Iqaluit during his Canadian trip aimed at healing and reconciliation with Indigenous groups and residential school survivors.
2024. An Air France Boeing 797-900 makes an emergency landing in Iqaluit due to a burning smell reported by passengers.
(Next story: The military exercise “Amalgam Chief”: B-52 bombers in northern Canada)
For more real life stories as a FSS in Iqaluit, click on the following link: Flight service specialist (FSS) in Iqaluit